Introduction:
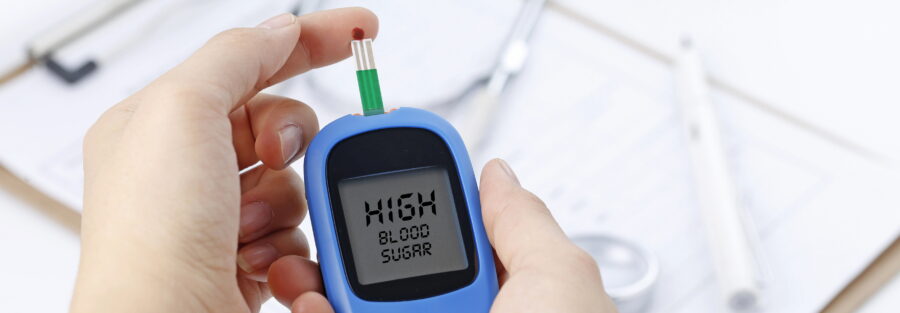
Glucose testing is a cornerstone in the realm of healthcare, offering insights into the delicate balance of blood sugar levels that play a vital role in overall well-being. From managing diabetes to preventive screenings, glucose testing provides a window into metabolic health. In this blog, we’ll delve into the intricacies of glucose testing, exploring its significance, types, and the proactive role it plays in maintaining optimal health.
Understanding Blood Glucose:
1. The Role of Glucose in the Body:
Glucose, a type of sugar, is the primary source of energy for our cells. It is derived from the breakdown of carbohydrates in the food we consume and is essential for the proper functioning of various bodily processes.
2. The Importance of Blood Sugar Regulation:
The body tightly regulates blood sugar levels to ensure a steady and controlled supply of energy. Insulin, a hormone produced by the pancreas, facilitates the uptake of glucose by cells, keeping blood sugar levels within a narrow range.
Types of Glucose Testing:
1. Fasting Blood Sugar Test:
– Purpose: Measures blood sugar levels after an overnight fast.
– Significance: Helps diagnose diabetes and assess overall blood sugar control.
2. Oral Glucose Tolerance Test (OGTT):
– Purpose: Measures the body’s ability to process glucose.
– Procedure: Involves fasting, consuming a glucose solution, and periodic blood tests over several hours.
3. Hemoglobin A1c Test:
– Purpose: Provides an average of blood sugar levels over the past two to three months.
– Significance: Used for long-term diabetes management and risk assessment.
4. Random Blood Sugar Test:
– Purpose: Measures blood sugar levels at any time, regardless of fasting.
– Significance: Useful for quickly assessing current blood sugar status.
The Significance of Glucose Testing:
1. Diabetes Diagnosis and Management:
– Early Detection: Glucose testing aids in the early diagnosis of diabetes, enabling prompt intervention and management.
– Long-Term Monitoring: Regular testing helps individuals with diabetes and healthcare providers monitor and manage blood sugar levels for optimal health.
2. Gestational Diabetes Screening:
– During Pregnancy: Glucose testing is essential for identifying gestational diabetes, a temporary condition that can affect pregnant individuals.
3. Preventive Health Screening:
– Risk Assessment: Glucose testing is often included in preventive health screenings, allowing for the early identification of individuals at risk of developing diabetes.
Lifestyle and Preventive Measures:
1. Balanced Diet:
– Role: A well-balanced diet helps regulate blood sugar levels. Focus on whole grains, lean proteins, fruits, and vegetables.
2. Regular Exercise:
– Impact: Physical activity aids in blood sugar control and improves insulin sensitivity.
3. Maintaining a Healthy Weight:
– Significance: Weight management contributes to overall metabolic health and blood sugar control.
Conclusion:
Glucose testing serves as a beacon, illuminating the intricate dynamics of blood sugar and providing valuable insights for preventive health and disease management. By understanding the different types of tests, their significance, and incorporating proactive lifestyle measures, individuals can take charge of their metabolic health. Glucose testing is not just a diagnostic tool; it is a pathway to empowerment, guiding individuals towards choices that nurture a life of vitality and well-being.